
The latest figures from Invest Hong Kong 2025 show that the total number of local companies in Hong Kong has reached1,159,000 homesIn addition, more than 60% of them are engaged in international trade-related businesses. Behind this figure is the strategic choice of Chinese foreign trade enterprises to utilize Hong Kong's unique advantages for global layout.
What is more noteworthy is that Hong Kong reigns as the world's freest economy in 2025 and introduces the Companies (Amendment) Ordinance to optimize the business environment and provide easier access for enterprises in cross-border trade.Hong Kong companies do re-export trade, has become the standard configuration of foreign trade enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency, tax optimization.
This article will be from the practical point of view, in-depth analysis of foreign trade enterprises through the Hong Kong company for re-export trade, to realize theProfit maximization, tax optimization, capital securityThe threefold goal. If you need to register a Hong Kong company to do re-export trade welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (micro letter: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

.
01.Advantages of Hong Kong as an entrepot
A tax paradise with low tax rates and fewer taxes
- Profits tax:Hong Kong has territorial taxation and only taxes profits derived from Hong Kong at a rate of only 8.251 TP3T (for the first HK$2 million of profits) and 16.51 TP3T (for the excess).
- No turnover tax:Hong Kong does not levy turnover taxes such as value-added tax (VAT), business tax, consumption tax, etc.
- No capital gains tax:No tax on corporate investment income, asset appreciation
- No dividend tax:No tax on dividends to shareholders
Comparison: Mainland CIT 25% + VAT 13%, the combined tax burden is 2-3 times higher than Hong Kong!
Practical cases:
An electronic product exporter in Shenzhen, with an annual export volume of 30 million yuan, after re-export trade through a Hong Kong company:
- Mainland direct export model: tax payment of about $4.2 million
- Hong Kong re-export model: tax payment of about $1.65 million
- Annual tax saving effect: 2.55 million dollars
Second, the funds in and out of freedom, no foreign exchange control
- Freedom of movement of funds in and out of the country:Not subject to the Mainland's foreign exchange restriction of US$50,000 per person per year
- Multi-currency accounts:Hold 10+ currencies at the same time, including USD, EUR, HKD, etc.
- Receive and pay easily:PayPal, Stripe, and other international payment tools directly binding
- Facilitates the receipt of global customer payments:Circumventing trade restrictions on Chinese companies in some countries
- Exchange rate risk hedging:Use of Hong Kong financial instruments to lock in exchange rates
Special reminder: Starting from 2025, the Mainland's regulation of cross-border capital flows will be strengthened, and trade settlement through a Hong Kong company can significantly reduce the risk of having your bank account frozen.
III. Geographical and policy advantages
- Third largest financial center in the world with a good international reputation
- Free port status with basic duty-free entry and exit of goods
- Signing of the CEPA agreement with Mainland China, with zero tariff for some commodities
- Avoiding high anti-dumping duties on "Made in China" in some countries
IV. Greater recognition of international trade
Market research shows:
68%'s European and American buyers prefer to deal with Hong Kong companies
Hong Kong company letter of credit opening success rate higher than mainland companies 40%
Choosing Hong Kong for international dispute arbitration improves resolution efficiency by 50%
Fifth, the advantages of flexible operation: privacy protection + simple architecture
Registration Convenience:
Enrollment time: as fast as 6 hours for e-certificates
Registered Capital: No paid up, standard HK$10,000
Shareholder information: not publicly disclosed to protect business privacy
If you have a Hong Kong company registration, other overseas company registration, overseas structure building, cross-border e-commerce tax compliance needs, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

.
02.How to use Hong Kong companies for re-export trade?
Step 1: Structuring and Hong Kong Company Registration
Requirements for registering a Hong Kong company:
- At least 1 shareholder/director (may be the same person, no nationality restrictions)
- Hong Kong registered address (we can provide)
- Statutory Secretary (must be a Hong Kong licensee)
- Company name ending in "Limited"
- Important Notes: If a mainland company plans to inject capital or take a controlling interest in a Hong Kong company, it must do so in advance.ODI FilingOtherwise, the funds cannot leave the country in a compliant manner. 2026 OFAC verification will be tightened, and direct remittance without filing will be intercepted by banks.
Step 2: Trade process design and document management
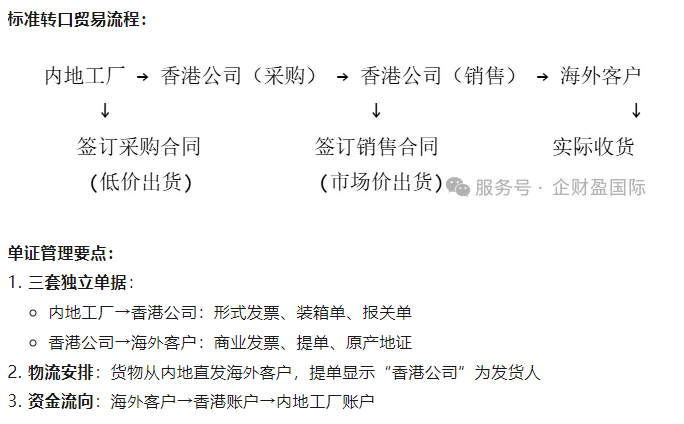
Step 3: Hands-on case studies
Case: Dongguan a furniture factory re-export trade whole process
Business Background:
- Annual export value: 50 million RMB
- Main Markets: USA, Europe
- Products: Solid wood furniture
- Pain point: U.S. tariffs 251 TP3T, profits are being severely squeezed
Solution:
- architectural design
- Registration of Hong Kong "XX International Trade Company Limited"
- Dongguan factory signed with Hong Kong companyexclusive supply agreement
- ODI filing, investment of HKD 1 million as registered capital
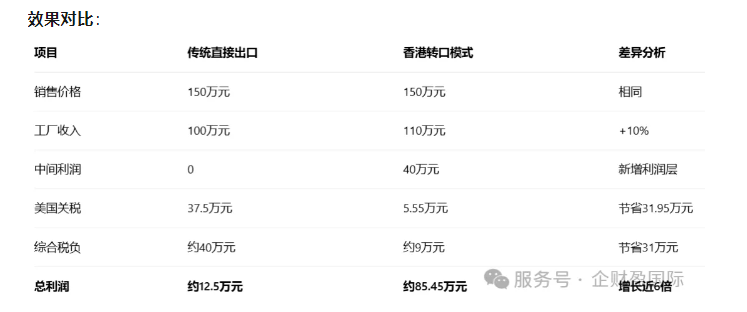
- Price strategy adjustment
- Sales price: 1.5 million yuan/lot
- Hong Kong company book profit: $400,000
- Ex-factory price: 1 million yuan/lot
- Invoiced price: $1.1 million (including 10% profit)
- Dongguan factory toCost price + 10% profitSold to a Hong Kong company
- Hong Kong companies are based onmarket priceSelling to American Customers
- Logistics and Documentation
- Logistics path: Dongguan → Yantian port → Los Angeles port (direct)
- Consignor of bill of lading: Hong Kong XX International Trading Co.
- Certificate of Origin: Application for "Hong Kong Transit Certificate"
- U.S. tariffs: from 25% to3.7%(General MFN rate)
- where the money is flowing
- U.S. client pays $1.5 million into HSBC account in Hong Kong
- Hong Kong company pays $1.1 million to Dongguan factory account
- Profit retention: $400,000 left in Hong Kong account
If you have a Hong Kong company registration, other overseas company registration, overseas structure building, cross-border e-commerce tax compliance needs, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

Let's take another detailed case study:
Let's say your company's primary customers are from the United States, and you currently have an order for $1 million in apparel, and let's say the cost of the apparel is $600,000, then your company could be in one of two situations:
1) Those who have the right to import and export, and have factories of their own, so that they can produce and sell their own products;
(2) Without import and export rights, after purchasing in domestic factories, all of them are entrusted to foreign trade companies for export.
The first situation, the original operation is a very simple bilateral trade, mainland companies directly in the mainland customs export, the United States received the goods directly after the T / T back to the domestic, then do not count the other costs, your company will have a 400,000 U.S. dollars in profit.
Taxes are already high by paying corporate income tax at the state's required rate, not counting other taxes due, plusChina has foreign exchange control, even if a company has the right to import and export and has a US dollar account, there is a limit to its use., the amount will be determined by the amount of your exports, that is to sayForeign exchange that exceeds the limit of the USD account will still be cleared into RMB and subject to settlement losses;
On the contrary, when you pay for imports, you have to purchase foreign exchange from the bank to pay for the amount of US dollars that exceeds the amount in your account.One in, one out, to the enterprise down the year to the settlement of foreign exchange losses is also very large.
If it is operated with a Hong Kong company:
It is to register a Hong Kong company as a transit place, use the Hong Kong company and foreign customers to sign contracts as well as orders, and then through the name of the Hong Kong company from the domestic factory to buy goods.
Foreign customers can pay directly to our Hong Kong company account, the Hong Kong company's account and then directly transfer the purchase price to the domestic factory, while the profit is retained in the Hong Kong company's bank account.
Specific operations:
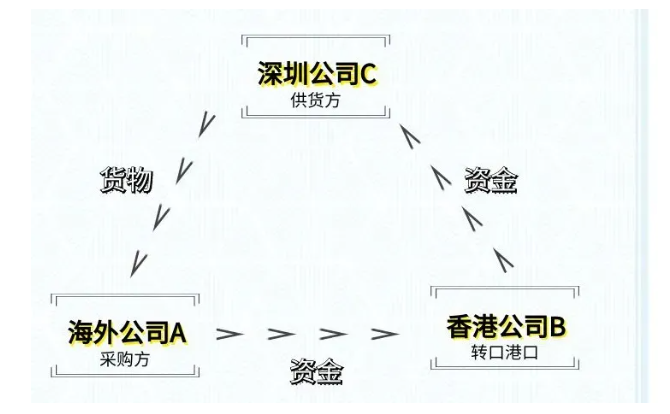
The customer is a U.S. company A, your Hong Kong company is B, B first to your Shenzhen company C into the goods, the cost is 600,000 U.S. dollars. Then sell the goods to our U.S. company A, the selling price is 1 million U.S. dollars.
Shenzhen company C will be the goods directly from the domestic shipments to the U.S. company A there, then the U.S. company A according to the terms of the contract, he will be the payment of $ 1 million directly to your Hong Kong company's account inside.
And your Hong Kong company B will then transfer the purchase cost of 600,000 U.S. dollars to your Shenzhen company C's company account inside.
Then this operation can actually avoid the loss difference between the exchange rates and also facilitate tax planning.
This is because the $400,000 in profits you retain in Hong Kong Company B can actually be claimed as an overseas profits exemption, which can save a large amount of tax costs.
Need to pay attention to the issue of customs clearance, in the process of re-export trade, company A needs to take the contract signed with the Hong Kong company B for customs clearance, the contract needs to be specified above the place of receipt of goods for the overseas company C.
Once the contractual issues are clear, people will consider the logistics and financing of the trade.
Let's start with the logistics, the shipment is still going from the mainland to the US
The specific operation is your mainland company has the right to import and export, first take his contract with the Hong Kong company to declare customs, many people will ask thatMy goods are sold from mainland China to Hong Kong, can I ship them directly to the US?
Here to explain clearly, the contract specifies that the place of receipt is a U.S. port, as long as you specify, go to the customs declaration is no problem. Because where to ship the goods is not any relationship, this is just between the two companies business behavior.
Go to the customs declaration of goods products, quantity, value, transported there, certificate of origin, all the documents are complete, the goods can be handed over to the shipping company, to help you do a SHIPPING action. Without these things, the shipping company is no one dares to take this order to help you ship away, no customs declaration is smuggling, so before you find the shipping company, you have to go to do the whole procedure of customs declaration.
After customs clearance to the shipping company, you freight to the pier mouth, the shipping company to load the ship container, on board, buy insurance, sail, ship away. Then when the ship leaves.The shipping company has a bill of lading that goes to your mainland company. Your mainland company speed-delivers the document to the United States.
But because all the signatories on these bills are Hong Kong companies, so at this time he must do an endorsement procedure, which is what we call the procedure for changing the bill of lading, that is, changing a consignor.
So, one asks.That my goods if I go to Hong Kong to change the bill of lading that is not very troublesome? In fact, this is not necessary, the goods do not go to Hong Kong, the Hong Kong company is your own, this change bill of lading is actually your own change. I changed the bill of lading, do an endorsement, endorsement of the documents speed delivery to the United States, the U.S. customers will be able to go to the terminal to receive goods.
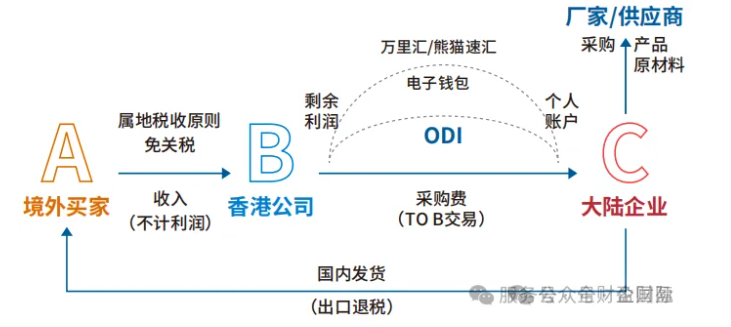
What about financial flows?
First of all, the U.S. customers receive the goods will be in accordance with the Hong Kong company signed the order will be 1 million U.S. dollars T / T to your Hong Kong company account, and then the Hong Kong company will be in accordance with the mainland company signed the procurement contract, will be 700,000 U.S. dollars back to the country to do foreign exchange write-offs, this step after the operation of the mainland company, the mainland company's tax base will be lowered from the original 400,000 U.S. dollars for 100,000 U.S. dollars, and the other retention of Hong Kong company's 300,000 U.S. dollars in profits.There is no tax to pay after applying through overseas profits, giving you a much lower tax cost.
If you have a Hong Kong company registration, other overseas company registration, overseas structure building, cross-border e-commerce tax compliance needs, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

.
03.How to transfer profits from Hong Kong company's re-export trade back to the Mainland in a compliant manner
The compliant repatriation of profits from Hong Kong companies' re-exports to the Mainland is the most concerned and confusing aspect for many foreign trade entrepreneurs. The core of compliant repatriation lies inSatisfying the Mainland's foreign exchange control, tax declaration and business substancerequirements, while ensuring that financial flows are transparent, legal and accountable.
Below is a detailed breakdown of the 5 mainstream compliance paths, their key operational points and tax implications, along with a "combo" strategy to help you choose the best option for your business.
.
Route 1: Service fee/commission payment (most common and flexible)
This is the most direct and common way of repatriating profits to Hong Kong through the provision of substantive services by Mainland companies to Hong Kong companies.
- operating method::
- conclude: Mainland affiliates enter into Marketing Service Agreements, Management Consulting Service Agreements or Commission Agreements with Hong Kong companies.
- Provision of services: Mainland companies are required to actually fulfill the content of the agreement (e.g. market research, customer maintenance, order coordination, etc.) and keep evidence such as work records, emails and reports.
- invoicing: Mainland companies issue VAT invoices to Hong Kong companies (usually "modern service industry" invoices of 6%).
- disbursements: The Hong Kong company remits the payment to the Mainland company's counterpart foreign exchange account according to the invoice amount.
- tax treatment::
- value-added tax (VAT): Usually 6%.
- corporate income tax: Pay tax at the rate of 25% on the company's profits.
- fact: The service fee paid can be used as a Hong Kong company'spre-tax costfull deduction, thereby lowering Hong Kong's profits tax.
- mainland China (PRC excluding Hong Kong and Macau, but including islands such as Hainan): Mainland companies are required to pay a service fee for the services they receive
- value-added tax (VAT): Usually 6%.
- corporate income tax: Pay tax at the rate of 25% on the company's profits.
- vantage: Clear processes, well justified financial transactions, clear tax treatment, and the most maneuverable.
- crux::Pricing of services must comply with the "arm's length principle", i.e., the charges should be comparable to the provision of similar services to unrelated third parties, and it is usually recommended to keep it in the range of 15%-30% of gross profits to avoid being challenged by the IRS as transfer pricing.
.
Path 2: Shareholder dividends (suitable for long-term investment returns)
Distribute the after-tax profits of a Hong Kong company to mainland shareholders in the form of dividends.
- operating method::
- strategic decision: A Hong Kong company holds a directors' and shareholders' meeting to make a resolution on dividends.
- payee: Hong Kong companies remit dividends to the personal or corporate accounts of mainland shareholders in accordance with the resolution.
- declare (to customs): Mainland shareholders are required to file tax returns on their own initiative.
- tax treatment::
- If the shareholder is a Mainland company: Under the Mainland and Hong Kong Tax Arrangement, such dividend is exempt from enterprise income tax in the Mainland (subject to conditions such as shareholding ratio ≥25% and continuous holding for 12 months). Otherwise, the dividend is subject to tax at the rate of 25%, but the profits tax already paid in Hong Kong can be credited as provided.
- If the shareholder is a natural person from the Mainland: need to press20% rate to pay personal income tax. This isHighest tax costsOne way to do this.
- fact: Dividend distributionneedlessPayment of withholding tax in Hong Kong.
- mainland China (PRC excluding Hong Kong and Macau, but including islands such as Hainan)::
- If the shareholder is a Mainland company: According to the Mainland and Hong Kong Tax Arrangement, the dividend is exempted from enterprise income tax in the Mainland (subject to conditions such as shareholding ≥ 25% and 12 consecutive months of shareholding). Otherwise, the dividend is subject to tax at the rate of 25%, but the profits tax already paid in Hong Kong can be credited accordingly.
- If the shareholder is a natural person from the Mainland: personal income tax is payable at the rate of 20%. This is one of the highest tax costs.
- vantage: The legal procedures are clear and suitable for a large one-off repatriation after the profits have been retained in Hong Kong for a long period of time.
- drawbacks: Heavy tax burden on natural person shareholders and the funds go directly into the shareholders' personal accounts, making it inconvenient to use them for the company's operations.
.
Route III: Payments under trade (most hidden and natural)
The "wrapping" of profits in normal trade payments applies where there is a genuine transaction of goods between a Hong Kong company and a Mainland related company.
- operating method::
- Adjustment of pricing: In procurement contracts between Mainland affiliates and Hong Kong companies.raise appropriatelyThe unit price at which the goods are sold.
- Payment of goods: The Hong Kong company pays the mainland company the amount comprising the profit in the name of "purchase money".
- tax treatment::
- fact: Higher procurement costs can reduce the taxable profits of a Hong Kong company.
- mainland China (PRC excluding Hong Kong and Macau, but including islands such as Hainan): Mainland companies are required to provide information onfull payment(Revenue (including profit component) is recognized and subject to value-added tax (13%) and corporate income tax.
- vantage: The flow of funds is fully aligned with the main business, which is hidden and has a natural flow.
- Risks and key points::Price adjustments must be measured. Purchase prices significantly higher than market prices are highly susceptible to being challenged by both the Mainland and Hong Kong tax authorities as transfer pricing and face tax adjustments and penalties. It is usually recommended that the price fluctuation is within the upper limit of the reasonable market range.
.
Route 4: Affiliated business lending (suitable for short-term fund deployment)
The Hong Kong company lends funds in the form of a loan to a mainland affiliate, which is subsequently repaid.
- operating method::
- conclude: Sign a formal Loan Contract specifying the amount borrowed, term, interest rate and repayment schedule.
- Payment of interest: The Mainland company pays interest to the Hong Kong company on a regular basis.
- Repayment of principal: Repayment of principal upon maturity of the contract.
- tax treatment::
- Interest paid by mainland companies is deductible before tax (subject to debt-to-capital ratio limitations, usually the linked debt-to-capital ratio does not exceed 2:1).
- Subject to VAT withholding at the rate of 6% and EIT at the preferential rate of 10% or tax treaty.
- fact: Interest income received by a Hong Kong company is subject to Hong Kong profits tax (8.25%/16.5%). However, the interest can be used as finance charges for the Mainland borrowing company.
- mainland China (PRC excluding Hong Kong and Macau, but including islands such as Hainan)::
- Interest paid by mainland companies is deductible before tax (subject to debt-to-capital ratio limitations, usually the linked debt-to-capital ratio does not exceed 2:1).
- Subject to VAT withholding at the rate of 6% and EIT at the preferential rate of 10% or tax treaty.
- vantageThe nature of the funds is "liabilities" rather than "profits", which does not involve the high tax burden of profit distribution, and the funds can be used flexibly for the turnover of mainland companies.
- crux::Interest rates must be fairIn addition, reference should be made to the benchmark interest rate for similar loans or market interest rate published by the People's Bank of China for the same period, which may be adjusted to increase profits if too low, and interest expenses are not deductible before tax if too high.
.
Pathway 5: Reinvestment (with a long-term perspective)
Instead of transferring profits directly back to the Mainland, they are reinvested in the Mainland and enjoy preferential policies on foreign investment.
- operating method::
- direct investment: A Hong Kong company acts as a foreign investor in the establishment of a new or additional foreign-invested enterprise (WFOE) in the Mainland.
- Investment Areas: Invest in industries encouraged by the State, such as high-tech and modern service industries.
- tax treatment::
- The act of investing itself does not create an immediate tax liability on repatriation.
- Newly-established foreign-funded enterprises can enjoy tax incentives such as "two exemptions and three halves" (subject to the latest policy).
- vantage: There is no immediate tax liability and the funds are used to expand production and can be treated as foreign investment.
- drawbacks: The funds are not actually "returned" to the original shareholders or the company, but rather new assets are created.
.
Practical strategy advice: the combination model
Savvy companies often use "combinations" rather than relying on a single channel:
"Service fee + trade payment" combination::
This is the most robust and efficient strategy. Passing most of your profits throughservice feecompliance shifting, as it is well justified and moderately taxed. At the same time, within a reasonable market range, through theSlight increase in purchase priceThe way to hide a part of the profit in the payment of goods in the natural return. This not only can control the overall tax cost, but also can make the capital flow mode more diversified and reduce the risk of tax audit.
important reminder::
- ODI filing is a prerequisiteIf the initial registered capital of a Hong Kong company is from the Mainland, or if there is a subsequent capital increase, it must be completed before the funds leave the country.Outbound Direct Investment (ODI) FilingThis is the "passport" for the compliant repatriation of profits to the Mainland. This is a "pass" for profits to be returned to the Mainland in a compliant manner, otherwise all subsequent paths of return may be blocked.
- Business substance is fundamental: Whichever route is chosen, it must be supported by real business activities, contracts, documents and financial flows to ensure that the "three flows" (contractual, goods/services and financial flows) are integrated.
- Seek professional support: Cross-border tax planning is complex and it is highly recommended to consult with a tax consultant like us before proceeding.QCYA professional organization like this. We can design an optimal, verified compliance repatriation program tailored to your specific business model, shareholding structure and capital needs.
If you have a Hong Kong company registration, other overseas company registration, overseas structure building, cross-border e-commerce tax compliance needs, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!


- Hong Kong Company Registration Requirements
- Hong Kong Company Registration


