
hillsidesIn 2024, the number of foreign-owned factories in Vietnam surpassed 23,000, but the number of37%'s Chinese firm pulls out at a loss in three years due to poor site selection and tax treading waterThe
Samsung relies on industrial clusters in Bei Ninh province to save 15% in logistics costs per year, Foxconn escapes EU carbon tax snipes by virtue of Hai Phong city's "zero-tariff park", while more SMEs are trapped in "policy traps" and "cultural divides". "China--"It's not that Vietnam is unprofitable, it's that your map is drawn wrong" .
This article combines the internal data of Vietnam's Ministry of Industry and Trade, 12 real cases of stepping on the pitfalls, to dismantle from the site selection to the production of theFull Process Survival ManualThe
.
01.Site selection is important for building a factory in Vietnam
1. North Vietnam-Mature industry chain, close to China
✅ Location advantage:
✔️ The northern part of the region borders China's Guangxi and Yunnan, which facilitates import and export trade and supply chain integration with lower logistics costs.
✔️ Hai Phong Port is the main port in the north with large throughput capacity, suitable for raw material import and product export.
✔️ The northern region has a mature labor market and a cost advantage over the south for labor-intensive manufacturing.
✔️ Hanoi and neighboring areas provide various tax exemptions and support policies, especially for electronics and heavy industry enterprises.
✅ Suitable industries: electronics manufacturing (e.g., electronic components, smart devices), machinery manufacturing, heavy industry (e.g., auto parts, steel, etc.)
✅ Representative industrial parks
Thang Long Industrial Park, Hanoi
Que Vo industrial area in Bei Ninh
Nomura Industrial Park in Haiphong
.
2. Central Viet Nam--Low cost and resourceful
✅ Location advantage:
✔️ The central part of the country, such as Da Nang and Hue, is a pivotal zone connecting the north and the south with convenient logistics, making it an important hub for import and export enterprises.
✔️ Da Nang Port is the third largest port in Vietnam with advanced equipment and high efficiency in cargo transportation, which can quickly connect domestic and foreign markets.
✔️ The labor market in the central region is abundant and qualified, suitable for labor-intensive and processing manufacturing.
✔️ The central region has more land and a favorable climate for the development of textiles, agro-processing, furniture manufacturing and other industries.
✅ Suitable industries: textile and apparel, chemical processing, agricultural and food processing, wood and furniture manufacturing
✅ Representative industrial parks
Lien Chieu Industrial Park in Da Nang
Phu Bai Industrial Park in Hue
Tam Thang Industrial Park in Quang Nam
.
3. South Viet Nam-The strongest economy with a large market
✅ Location advantage:
✔️ Ho Chi Minh City is the economic core of Vietnam, and the southern region has the largest number of industrial parks and export processing zones, making it suitable for the development of market- and logistics-dependent industries.
✔️ The southern region is home to a large number of multinational corporations and ancillary enterprises, with well-established supply chain facilities that can provide comprehensive manufacturing and logistics support.
✔️ Ho Chi Minh City and neighboring provinces are densely populated and have mature consumer markets, facilitating the manufacturing and distribution of consumer goods.
✔️ includes the Tan Son Nhat International Airport, several major ports (e.g., Gemini Port), and is capable of supporting efficient international logistics.
✔️ The southern region has more highly skilled labor and technicians, which is particularly suited to companies in the high-tech and electronics industries.
✅ Suitable industries: light industry (e.g. home appliances, apparel, plastic products, etc.), consumer goods manufacturing, electronic technology, food and beverage
✅ Representative industrial parks
Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone in Ho Chi Minh City
VSIP Industrial Park in Binh Duong
Amata Industrial Park, Tong Nai
.
Overall, Vietnam's industrial zones are widely distributed, with each region having its own specific industrial development direction and advantages. The northern region has become an important base for electronics manufacturing and auto parts due to its low-cost labor and geographical advantage of being close to China; the central region focuses on light industry and textiles and garments; and the southern region has become an important base for high-tech manufacturing and consumer electronics due to its well-developed infrastructure and market radiation capacity.
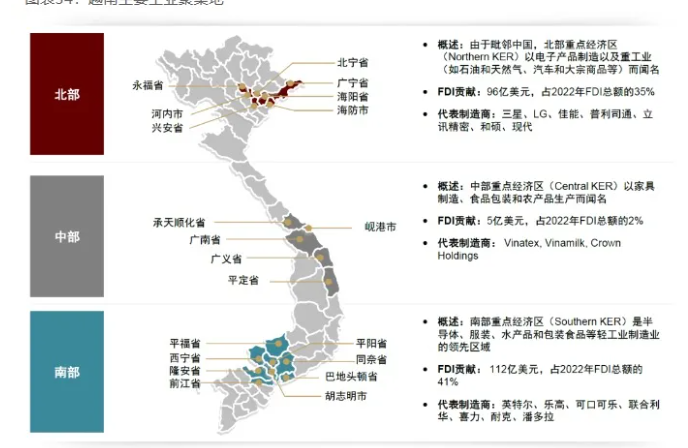
Figure 1: Current status of investment in the three main regions of Vietnam
In the case of Lixin Precision's investment project in the province of Bac Giang, for example, the site was selected based on a number of factors, including geographic location, supplier clusters and tax incentives offered by the government.
- Location:One of the key reasons why Luxon Precision chose to invest in a manufacturing base in the province of Bac Giang is its proximity to the Hanoi International Airport, which is only a 45-minute drive away. This provides great convenience for logistics and transportation and helps to reduce production and operating costs.
- Vendor clusters:The fact that Beijiang Province has an existing supplier cluster makes it easier for Lixin Precision to obtain the raw materials and components it needs. This cluster effect not only improves the efficiency of the supply chain, but also reduces procurement costs.
- Government tax incentives:The government of Beijiang Province has provided Lixun Precision with "supranational treatment", including a three-year tax exemption and a four-year 50% reduction in corporate income tax. These incentives have significantly reduced the operating costs of the enterprise and increased the return on investment.
Lucent Precision's investment project in the province of Bac Giang has achieved remarkable success, with the factory's capacity utilization reaching 85% one year after the investment, and annual revenue exceeding US$300 million. David Tran, head of PwC Vietnam, pointed out that the northern region is forming a complete electronics manufacturing ecosystem that will attract more than US$10 billion in investment over the next five years.
If you invest in Vietnam to build factories or need to register a company in Vietnam, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

02.Practical guide for project landing
The practical guide to landing a project to build a factory in Vietnam can be divided into three phases, and the timetable for each phase is as follows:
1,Phase 1 (1-2 months):
- Investment license application:The investor needs to submit an application for an investment registration certificate to the provincial planning and investment department or industrial park authority. This process usually takes 15 days, but may take longer in practice. For projects that meet certain conditions, the approval time for an investment license may be shortened to 15 days.
- Company Registration:After obtaining an investment license, the investor needs to register the company. The application for an Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC) is usually completed within 3 working days.
- Tax registration:Within 10 days from the date of obtaining the investment license, the investor is required to register for tax purposes with the competent tax authorities.
2,Phase II (2-3 months):
- Building Permit Application:The investor needs to submit an application for a construction license to the Ministry of Construction or the relevant agency. The whole process usually takes 30 working days.
- EIA approval:Depending on the size of the project, the investor may need to conduct an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). The preparation and approval time of the EIA document varies depending on the complexity of the project, but usually takes a certain amount of time.
- Fire approval:All new commercial buildings are required to obtain an architectural design certification from the Fire Department, which is required for a construction permit.
3, Phase III (1 month):
- Equipment import license:The investor will need to apply for an equipment import license from the customs department, depending on the customs approval process.
- Labor License:It is handled by the Ministry of Labor, Injured Soldiers and Social Affairs of Vietnam, and relevant documents need to be prepared and submitted in advance.
- Operating License:After completing the above steps, investors are required to apply for an operating license from the relevant authorities to ensure legal operation.
By following the above steps, investors can smoothly move forward with their factory building projects in Vietnam. It is recommended to seek the assistance of professional consulting firms throughout the process to ensure that all procedures comply with Vietnam's legal requirements. At the same time, in order to build investment factories in Vietnam, it is also necessary to go through the preliminary in-depth investigation, localization cooperation, advance talent reserve and efficient construction management, in order to successfully achieve the goal of rapid production.
Figure 2: Feedback from selected Chinese firms in Vietnam on the cost side of the equation
If you invest in Vietnam to build factories or need to register a company in Vietnam, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

03.Major taxes and rates in Vietnam
Vietnam is a member of the WTO and applies uniform tax standards for both domestic and foreign enterprises, with different tax rates and reduction periods for items in different fields. The main taxes in the current tax system are: corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), import and export tax, special sales tax, personal income tax, resource tax, agricultural land use tax, non-agricultural land use tax, environmental protection tax, property tax, stamp duty, door license tax, etc.
[Corporate income tax]
Currently, the general corporate income tax rate in Vietnam is 201TP3 T. Enterprises are subject to an income tax rate of 32-501TP3 T on income derived from the search, exploration and development of oil, natural gas and precious and rare resources.
Foreign-funded enterprises meeting the relevant conditions are entitled to a 10-17% income tax incentive, and enjoy "four exemptions and nine halves" (i.e., enterprises are exempted from enterprise income tax for four years from the time of making profits, and halved for the following nine years) or "six exemptions and thirteen halves" preferential policies. "The preferential policies.
For projects with large scale of investment and high technological content, they can enjoy up to30year's income tax credit of 50%.
[VAT]
According to Vietnam's Law on Value Added Tax (VAT) and its related regulations, there are currently three VAT rates in Vietnam: 0%, 5% and 10%, and export processing enterprises are exempted from VAT on their exports.
[Special sales tax]
In accordance with Vietnam's Law on Special Sales Tax and its related regulations, Vietnam imposes special sales tax on certain products, imported goods and services.
- If a special sales tax of 751 TP3T is imposed on tobacco products, the
- Alcohol is subject to 35% or 65% (65% for beer) sales tax depending on the degree;
- A special sales tax of 35%-150% is levied on vehicles with less than 9 seats, depending on displacement;
- The tax burden for new energy hybrid vehicles is 70% for vehicles of similar displacement;
- The tax burden on biofuel vehicles is 50% of comparable displacement vehicles;
- Special sales tax on entertainment operations such as cabarets, casinos, golf courses, etc. ranging from 15%-40%
[Import and export tax]
At the end of each year, the Ministry of Finance of Vietnam updates the export tax rates and import tax rates for goods. Except for duty-free goods, the vast majority of goods imported into Vietnam are subject to import tax.
Import duty rates on goods are categorized into ordinary, preferential and ex gratia rates.
The preferential tax rate applies to imported goods originating from countries (territories) that grant Vietnam most-favored-nation status in trade relations.Vietnam's response to a request for information fromWTO (World Trade Organization)Committed preferential rates of duty are granted on imports by members.
The preferential duty rate applies to goods imported from countries (territories) that have signed Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with Vietnam.
Goods enjoying preferential tax rates are required to provide a certificate of origin (C/O), otherwise the ordinary tax rate applies, i.e., preferential tax rate x 150%.
[Personal Income Tax]
From July 1, 2020, the starting point of Vietnam's personal income tax exemption has been raised from a monthly income of VND9 million (about US$384) to a monthly income of VND11 million (about US$473), and if a family member has no income, the starting point of the monthly exemption has been raised by VND4.4 million (about US$189) for each additional member.
Households with monthly incomes exceeding the exemption limit are subject to personal income tax, which is based on progressive rates ranging from 51 TP3T to 351 TP3T.
Non-resident aliens are taxed only on income derived from Vietnam, with the rate of 25% applying in the first year and the foreign resident taxable rate applying in subsequent years.
Residents of countries with which Vietnam has signed double taxation agreements are exempted from paying individual income tax if they are resident Vietnamese taxpayers and meet certain conditions.
[Environmental protection tax]
Vietnam imposes environmental protection tax on some commodities (mainly gasoline and coal) that generate environmental pollution at the time of use, both at the production and import stages. For example, gasoline, diesel oil and lubricating oil are levied at VND 1,000-4,000 per liter or kilogram (about US$0.04-0.18), coal at VND 15,000-30,000 (about US$0.66-1.3) per ton, nylon bags at VND 50,000 (about US$2.2) per kilogram, and so on.
If you invest in Vietnam to build factories or need to register a company in Vietnam, welcome to sweep the code to add our online customer service (WeChat: jxhqcy890 / cell phone: 16625410105), to arrange for the manager to answer questions, provide professional advice and full one-on-one service!

- Vietnam
- external trade
- Vietnam Company Registration
- cross-border e-commerce


